Single nucleotide substitution in the seed region of miR96 induces a significant discordance in promyleocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF) transcript targeting To our knowledge, the SNP (rs) in miR96 is the first confirmed example of a novel target binding site being created by a SNP within a miRNA seed sequenceOtherwise reject R (0) i (3) For each region, find all points that arecompatible with the region · For the 1226 human miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region, 314 (256%) of them are located in miRNA clusters, whereas among the 1587 human miRNAs without SNPs in their seed region, only 3 (2%) of them are located in miRNA clusters (P = 606 × 10 −4, χ 2 test) (Table S2) miRNAs from the same cluster have the tendency to regulate the
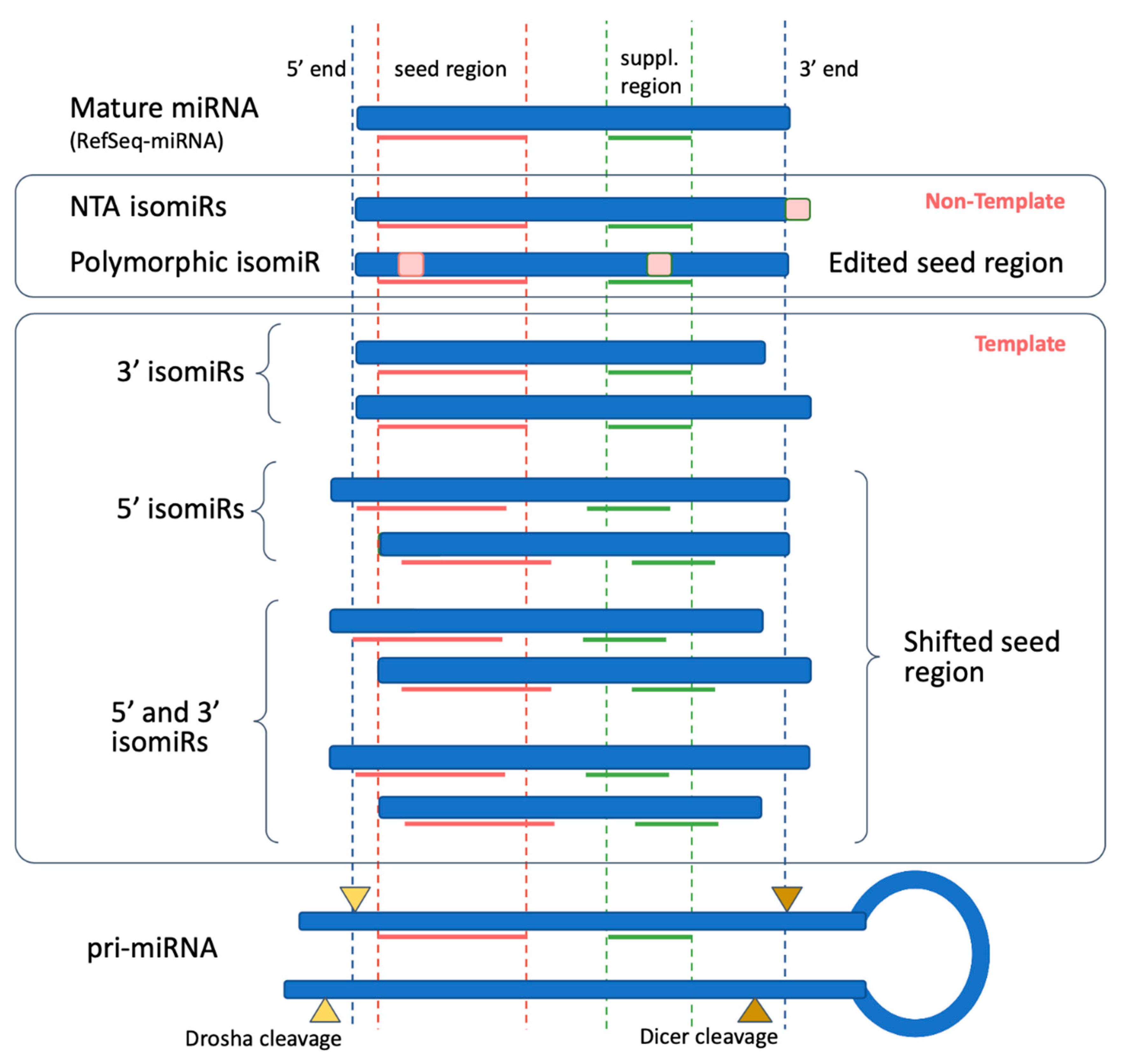
Biomolecules Free Full Text Isomirs Hidden Soldiers In The Mirna Regulatory Army And How To Find Them Html
Seed region mirna
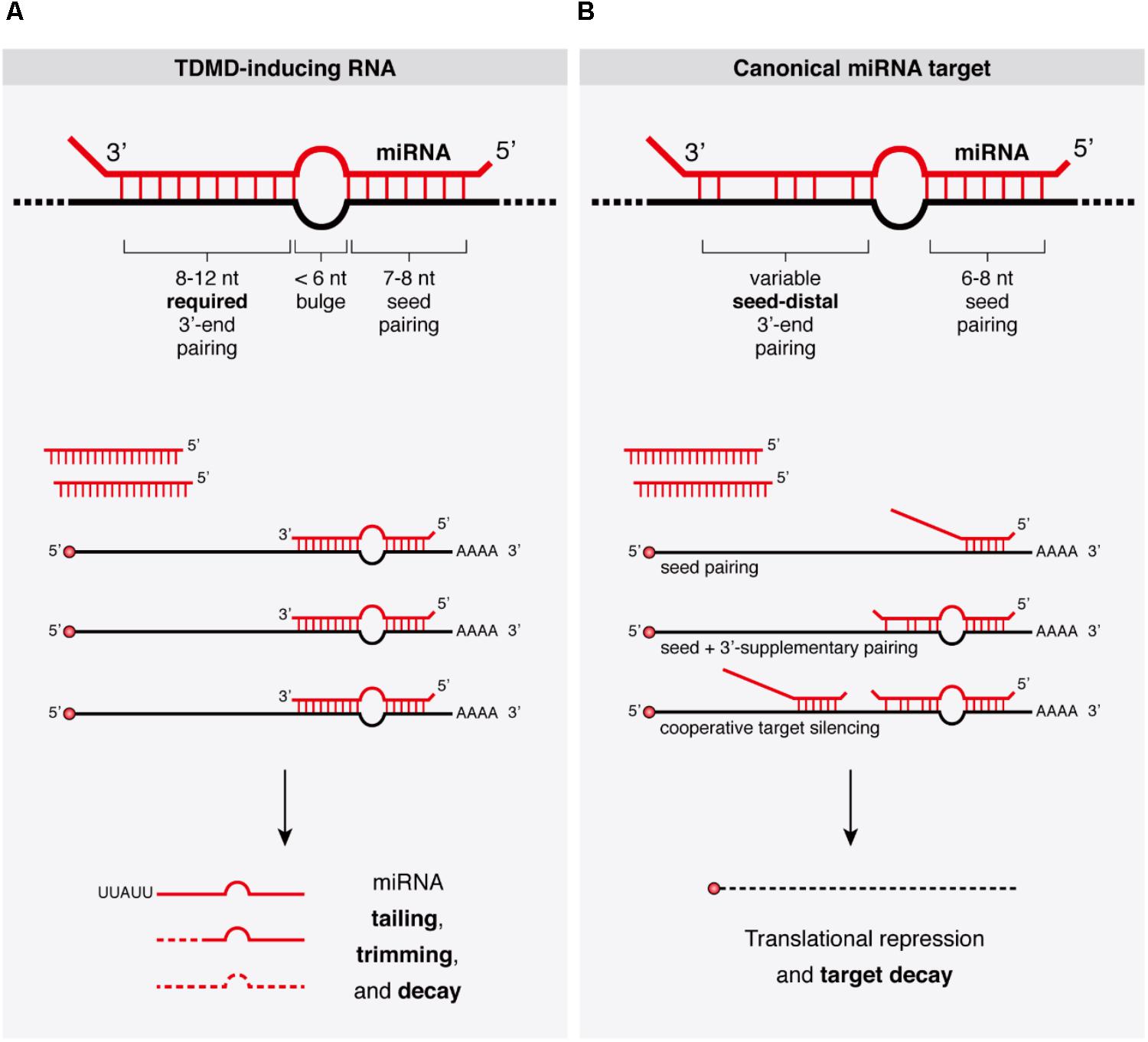
Seed region mirna- · In contrast to the miRNA 5′ (seed) region, the role of the 3′ region in miRNAtarget recognition is less defined Early evidence arose from reported cases of miRNA repression without perfect pairing in the seed region 13 In those cases, increased pairing in the 3′ region was observed (Fig 1 B)In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codonThe 3′UTR often contains regulatory regions that posttranscriptionally influence gene expression During gene expression, an mRNA molecule is transcribed from the DNA sequence and is later translated into a protein
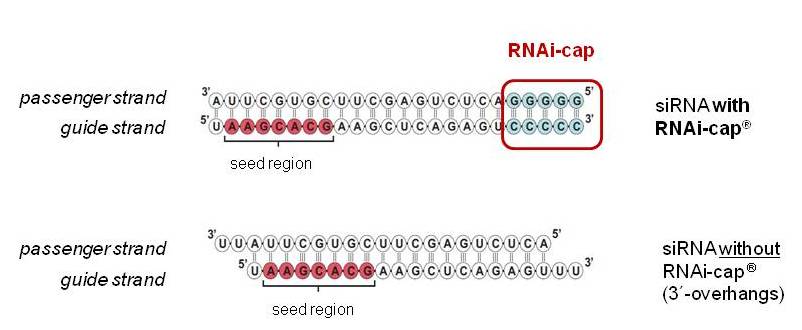


Riboxx Rna Technologies Better Silencing With Rnai Cap
(1) Partition the image into initial seed regions R(0) i (eg, split the image in 7x7 regions) (2) Fit a planar model to each seed region IfE(R(0) i, a, m) is small enough, accept R(0) i and its model; · miRNAs are small RNAs that guide Argonaute proteins to specific target mRNAs to repress their translation and stability Canonically, miRNA targeting is reliant on base pairing of the seed region, nucleotides 2–7, of the miRNA to sites in mRNA 3′ untranslated regions Recently, the 3′ half of the miRNA has gained attention for newly appreciated roles in regulating targetMiRNA的种子区域(seed region,一般为成熟miRNA的2到8位碱基)与mRNA的3'UTR严格配对; miRNA前体具有一定的二级结构; miRNA在组织分化发育过程中,都具有明显的时空表达特异性; 在肿瘤与其他疾病中有特征性的表达方式,可作为诊断标记物。
· 這個區域稱之為seed region 或 nucleus region。 MiRNA target site預測 通常預測miRNA target site都使用SmithWaterman algorithm,該方法是利用不同的參數調整,找到最大吻合的核咁酸區域,而利用此演算法的方法有: Miranda , PicTar , TargetScan 等等。 · The nucleotides 28 in miRNA are termed 'seed,' which is the most crucial region for target recognition The seed region undergoes WatsonCrick base pairing with 3'UTR of mRNAs The degree of mRNA destabilization differs according to the class of the target siteNucleotide 2 al nucleotide 8 del miRNA, detto regione seed Nelle piante mRNA bersaglio (a) complementarietà tra la sequenza seed del miRNA e il 3'UTR Questo per spiegare la "regione seed" come giustamente proposto da Ivana;
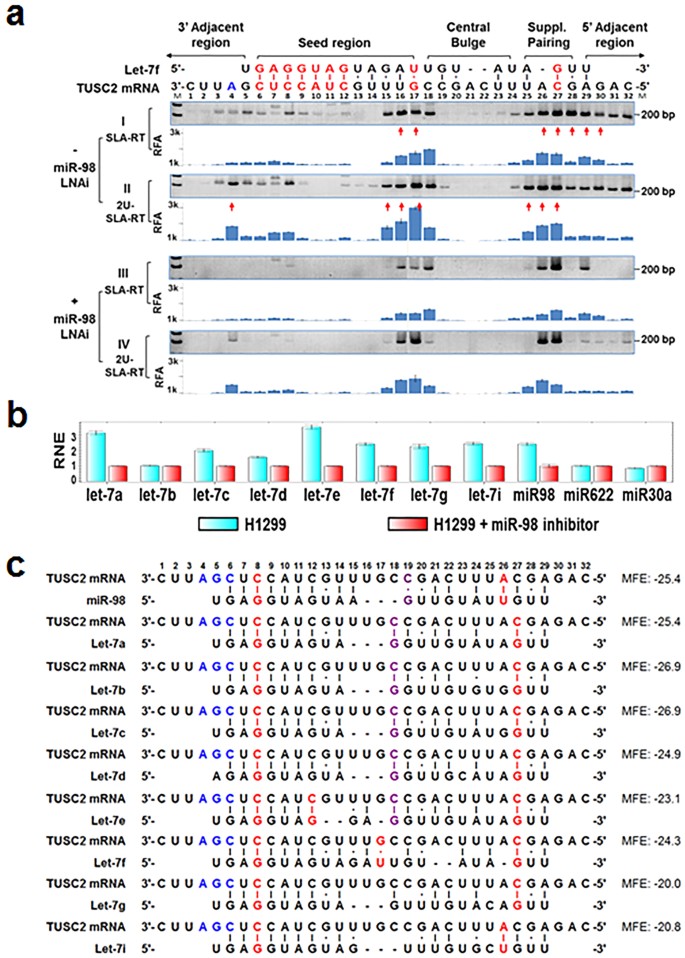
Keywords RNAi, Offtarget effects, Data analysis, Seed region, miRNA, siRNA, shRNA, Highthroughput screening Background RNA interference (RNAi) is a posttranscriptional gene regulatory mechanism 1 that has been widely used for functional genomics studies both in cell lines and organisms The synthetic duplexes referred to as small interLation inhibition and/or accelerated exonucleolytic RNA decay Most animal miRNAs display perfect pairing in the seed region, between nucleotides 2 and 8, and imperfect hybridization in the central region, between nucleotides 9 and 12 (Lewis et al, 05;(16) Mullany et al PLoS ONE microRNAs (miRNA) repress messenger RNAs posttranscriptionally through binding to the 3' UTR of the mRNA with the miRNA seed region It has been purported that longer seed regions have a greater efficacy on mRNA repression We tested this hypothesis by evaluating



Introduction To Micrornas Ibiology



Mirna Therapeutics A New Class Of Drugs With Potential Therapeutic Applications In The Heart Future Medicinal Chemistry
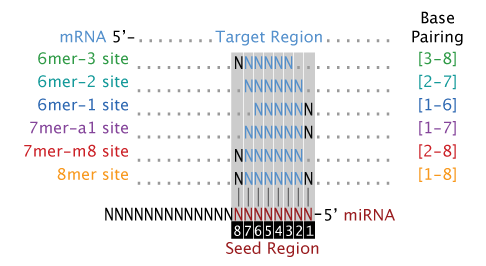
The latest version of/10/16 · Seed Pairing Is Enriched in miRNATarget Sites The miRNA sequence can be separated into five functional domains that affect miRNAtarget recognition 5′ anchor (nt 1), seed sequence (nts 2–8), central region (nts 9–12), 3′ supplementary region (nts 13–16), and 3′ tail (nts 17–22) (Wee et al, 12)MicroRNAs (miRNAs) bind to complementary sites in their target mRNAs to mediate posttranscriptional repression, with the specificity of target recognition being crucially dependent on the miRNA seed region Impaired miRNA target binding resulting from SNPs within mRNA target sites has been shown to lead to pathologies associated with dysregulated gene expression



Biomolecules Free Full Text Isomirs Hidden Soldiers In The Mirna Regulatory Army And How To Find Them Html



Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Sciencedirect
TargetScan is a target prediciton tool that predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer and 7mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA The target prediction software is frequently updated; · Die SeedSequenz ist die Sequenz (ca 68 Nukleotide) am 5' Ende der siRNA (oder miRNA), die quasi die "Bestimmungssequenz" für das Gen ist, welches stillgelegt werden sollInteressanterweise betrifft die Bedeutung der seedRegion va die 3'UTR und vollständige Komplementarität in der 5'UTR oder anderen Bereichen scheint nicht die Gleiche Relevanz zuFor miRNAs with low GC content of the seed region, noncanonical targeting was the dominant mechanism for target recognition In contrast to canonical targeting, noncanonical targeting did not lead to significant target downregulation at either the RNA or protein level Contact xwang@radoncwustledu
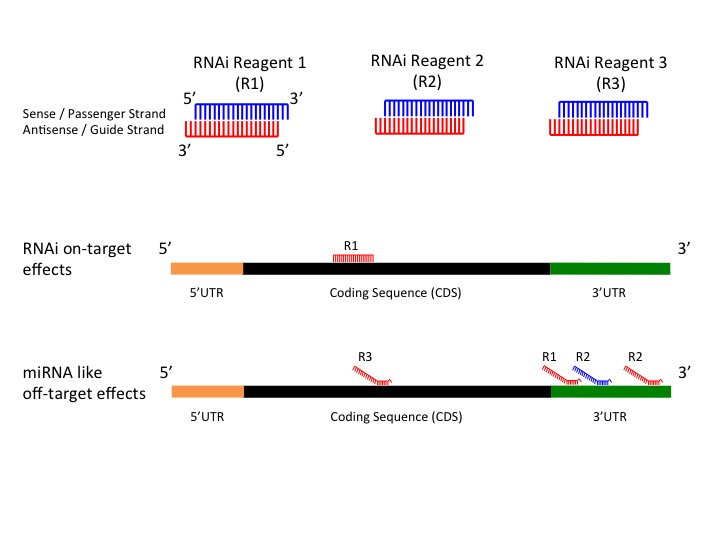


Gess


Insect Micrornas From Molecular Mechanisms To Biological Roles Part 2
In human miRNA seed regions and explore the clustering Clustered miRNAs with SNPs in the seed region Nonclustered miRNAs with SNPs in the seed region 0 10 30 40 50 Percent overlap (%) ⁎ Figure 2 Difference in the functional effect of SNPs in clustered and nonclustered miRNA seed regions ∗PBartel, 09) Because of this limited sequence complementarity, individual animal miRNAs appear to have multiple target transcripts (Bartel, 09), whereas · This region is known as "seedregion" and found at the 27 base of the miRNA This region is able to suppress the target mRNAs without having a
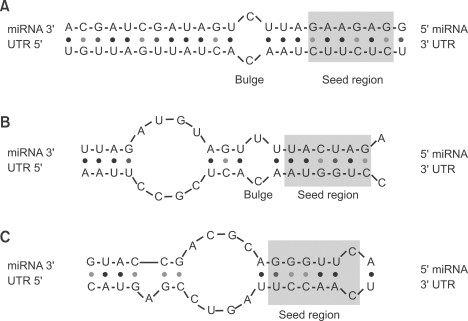


Got Target Computational Methods For Microrna Target Prediction And Their Extension Experimental Molecular Medicine
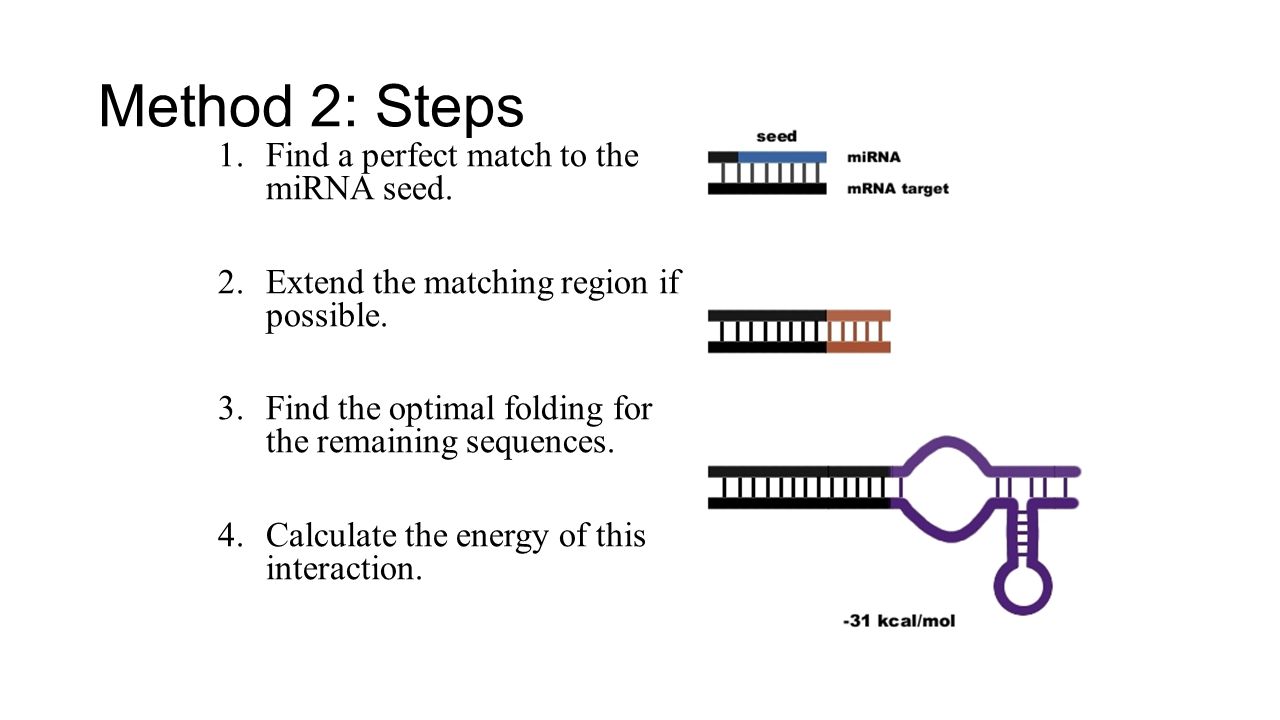


Microrna Computational Prediction And Analysis Ppt Download
Of the Ago2–miRNA–target complex show helix7 shifts to dock into the minor grove of the guidetarget duplex upon stable seed pairing (Fig 1B and D) Considering the close proximity of helix7 to the miRNA seed region and its apparent dynamic nature, we hypothesized that helix7 may be a structural element that shapes the binding properties of · The impact of miRNA seed types on target downregulation Previous studies have identified several major types of canonical miRNA target sites, including those matching to the 6mer, 7mer, or 8mer miRNA seed sequences (Table 2)Sequence conservation analysis suggested that target sites pairing to longer miRNA seeds are more conserved across species and thus are · At present, the major parameter that can explain the selection of the target mRNA and the efficiency of translation repression is the base pairing between the 'seed' region of the miRNA
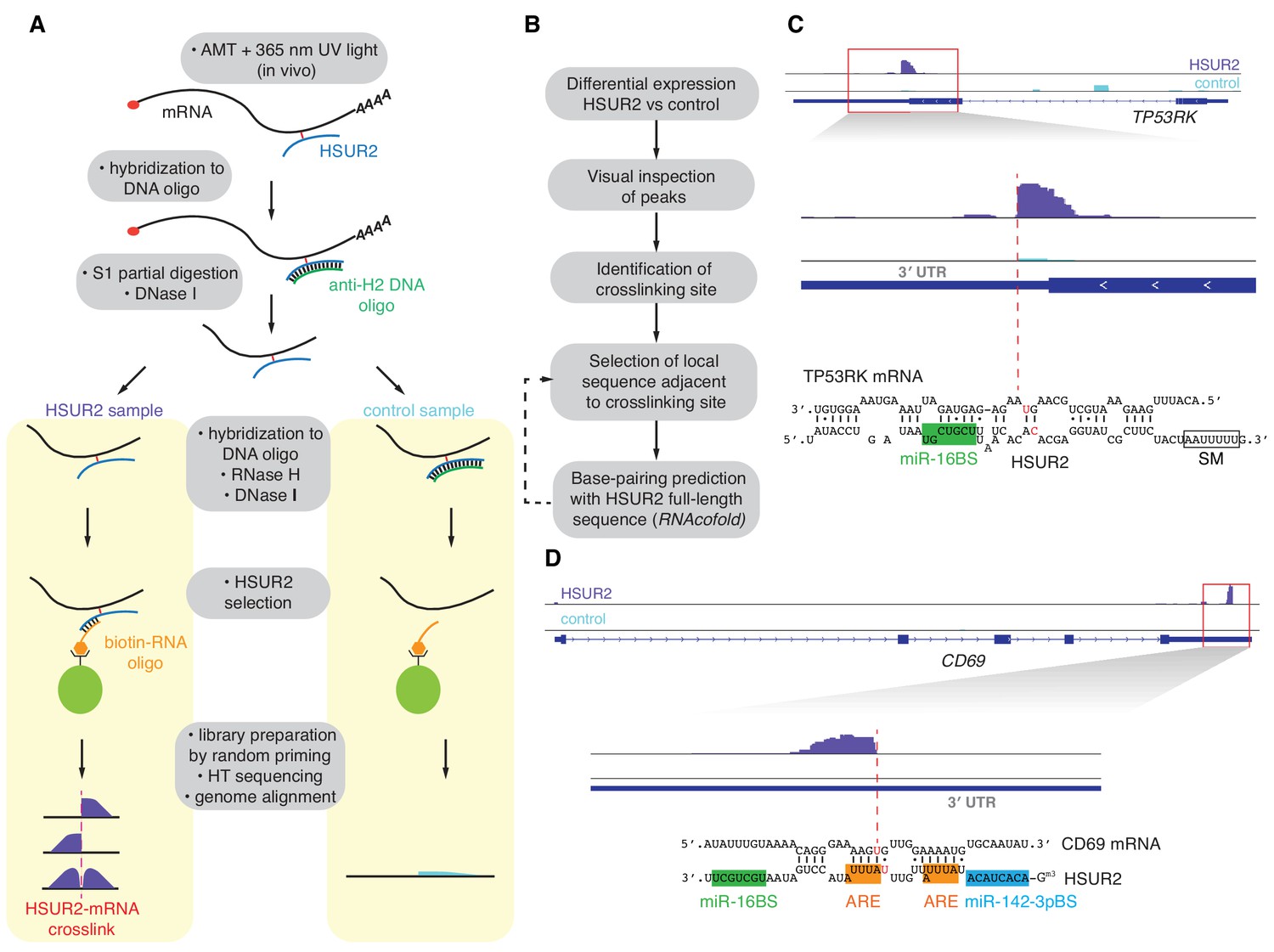


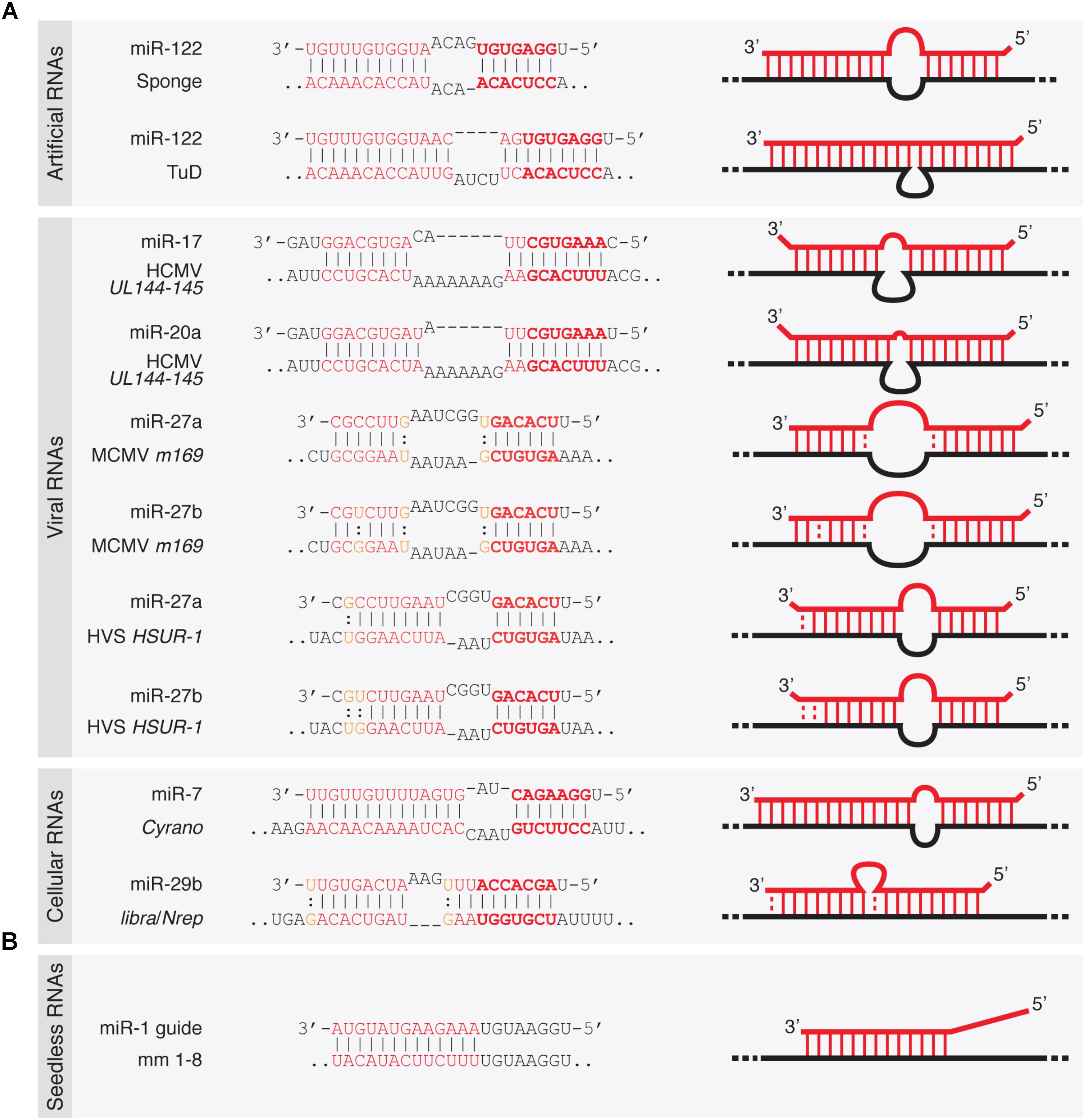
Viral Mirna Adaptor Differentially Recruits Mirnas To Target Mrnas Through Alternative Base Pairing Elife


Microrna The Small Molecule With A Big Story Promega Connections
Genomewide studies have revealed that the majority of editing events occur in noncoding RNA sequences, but little is known about their functional meaning MiRNAs are small noncoding RNAs that regulate the expression of target mRNAs with complementarities to their seed regionThe code is to get SNPs located in miRNA/premiRNA and their relationship(in loop, upstream of miRNA, downstream of miRNA, seed region or just in the miRNA) miRNA data is from mirBase while dbSNP data is from vcf file riverlee/miRNASNP · The set of luciferase activities compromised by miRNAmediated gene silencing at 5 nM miRNA concentration was obtained from Figure 1 Tm 2–8 value of the proteinfree seed region was calculated



An Evolutionary Perspective Of Animal Micrornas And Their Targets
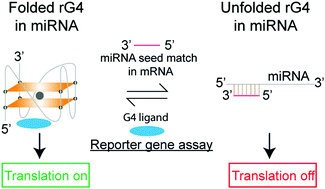


Structural Analysis Reveals The Formation And Role Of Rna G Quadruplex Structures In Human Mature Micrornas Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing
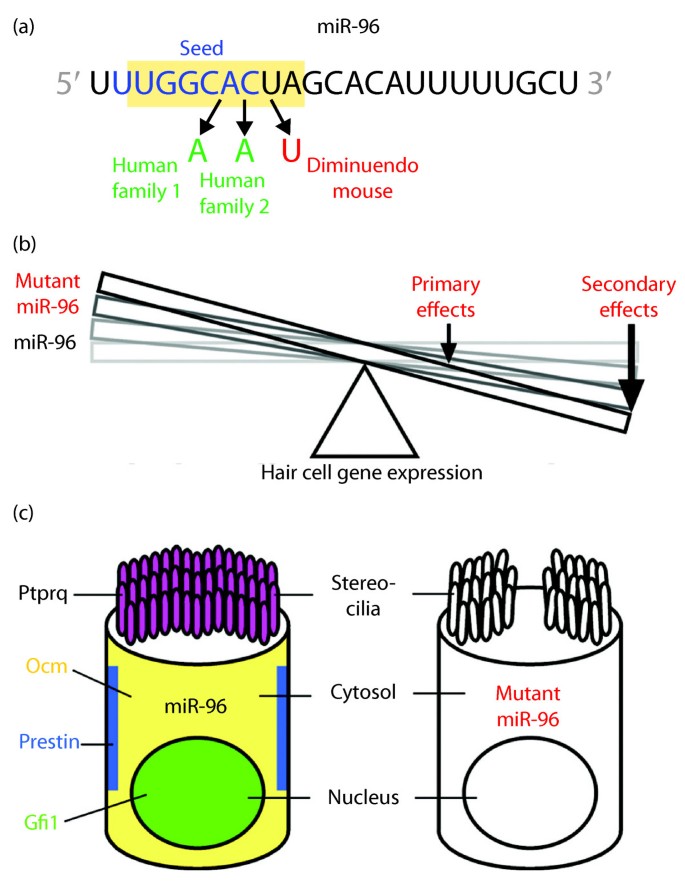
· Base pairing of the miRNA seed region (positions 2–8 from the 5′ end of an miRNA) in animals is critical for target recognition and repression (Bartel, 09;MicroRNAs, or miRNAs, posttranscriptionally repress the expression of proteincoding genes The human genome encodes over 1000 miRNA genes that collectively target the vast majority of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) Basepairing of the socalled miRNA "seed" region with mRNAs identifies many thousands of putative targetsMutations in the seed region of human miR96 are responsible for nonsyndromic progressive hearing loss Tamas Dalmay Related Papers A novel mutation within the MIR96 gene causes nonsyndromic inherited hearing loss in an Italian family by altering premiRNA



Systematic Prediction Of The Impacts Of Mutations In Microrna Seed Sequences



Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram
Ma che è diverso della sequenza seedThe most critical region for complementarity is the seed region (nucleotides 2–7 from the 5'terminus of the miRNA) 4,7 Aside from the seed region, other criteria have been established that can enhance miRNAmediated repression including complementarity at position 8 and the presence of an adenosine residue opposite the first miRNA · MicroRNAs (miRNAs) bind to mRNAs and target them for translational inhibition or transcriptional degradation It is thought that most miRNAmRNA interactions involve the seed region at the 5′ end of the miRNA The importance of seed sites is supported by experimental evidence, although there is growing interest in interactions mediated by the central region of the miRNA



Correlation Between Mirna Targeted Gene Promoter F1000research



A Cartoon Showing The Site And Mechanism Of Mirna Targeting To Mrna Download Scientific Diagram
Pasquinelli, 12) In contrast, most evidence indicates that miRNAs in land plants require more extensive pairing to their targets (Schwab et al, 05; · Analysis of experimentally validated miRNA targets demonstrated a similar trend, indicating a putative conserved mechanistic feature of seed regiondependent targeting mechanism These observations may prove useful as parameters for offtarget prediction algorithms and improve siRNA 'specificity' design rulesThe seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementary



Metazoan Micrornas Cell
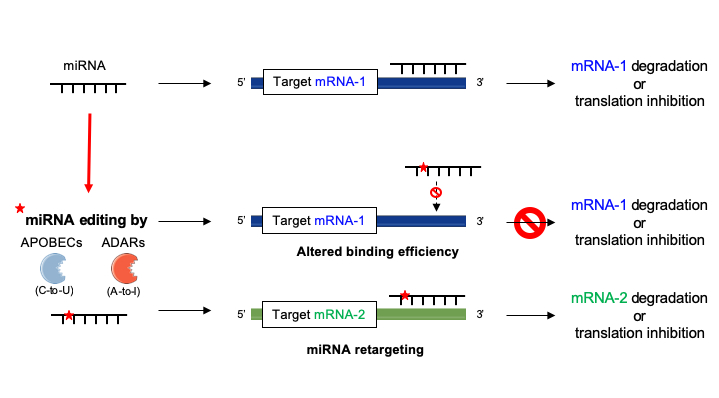


Ijms Free Full Text Deciphering Mirnas Action Through Mirna Editing Html
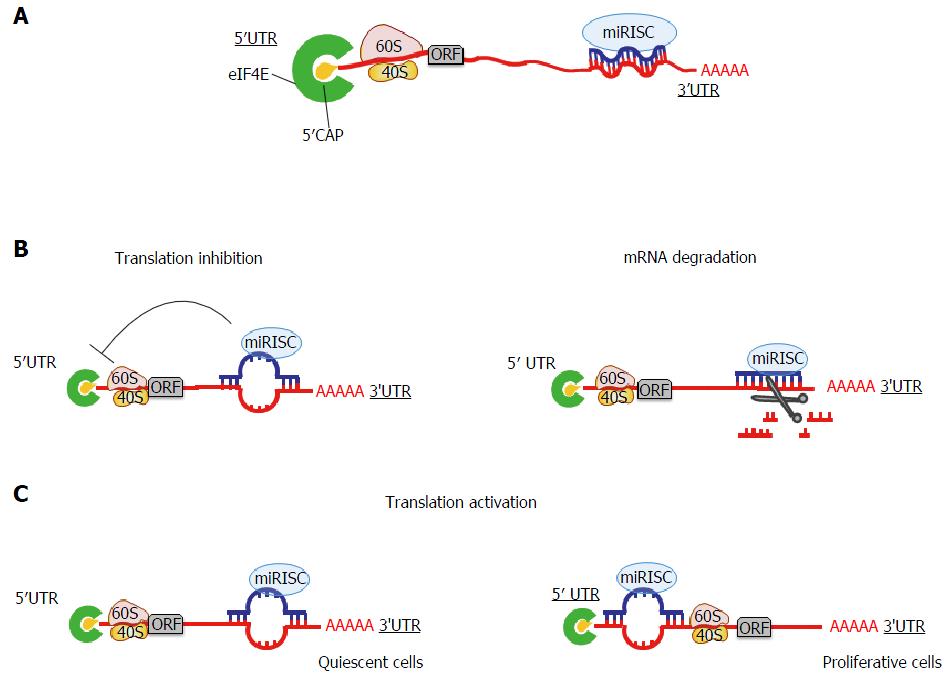
Bartel, 09) Because of this limited sequencecomplementarity, individual animal miRNAs apMicroRNA Editing in Seed Region Aligns With Cellular Changes in Hypoxic Conditions PubMed RNA editing is a finely tuned, dynamic mechanism for posttranscriptional gene regulation that has been thoroughly investigated in the last decade · In the RISC, the mature miRNA sequence allows interaction with the 3′untranslated region (3′UTR) of mRNA targets through canonical binding, namely, a partial sequence complementarity mediated by a 6–8 nt long region at the 5′ end of the miRNA called the 'seed', thus exerting its regulatory function via inhibition of protein translation or degradation of the mRNA


Mirvestigator Framework Detect The Mirnas Driving Co Expression Signatures



Not Mir Ly Small Rnas Big Potential For Micrornas In Therapy Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
TargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA (Lewis et al, 05) As an option, predictions with only poorly conserved sites are also provided · 种子序列(seed)位于miRNA的5'端第28nt,与靶基因的3'UTR是否可以形成配对,这个是判断miRNA靶基因的关键 保守性 miRNA的结合位点在多个物种之间如果有保守性,那么这个位点更可能是靶位点 热动力学 主要考察miRNAtarget对形成的自由能,自由能越低,可能性 · Moreover, mutation in miR1254 seed region did not abolish the inhibition on the luciferase activity of the reporter, which indicated the transcriptional regulation functioned through the nonseed region (Fig 3H, lane 3) We designed different mutants of miR1254 with mutations in nonseed region, and transfected them into HEK293 cells separately



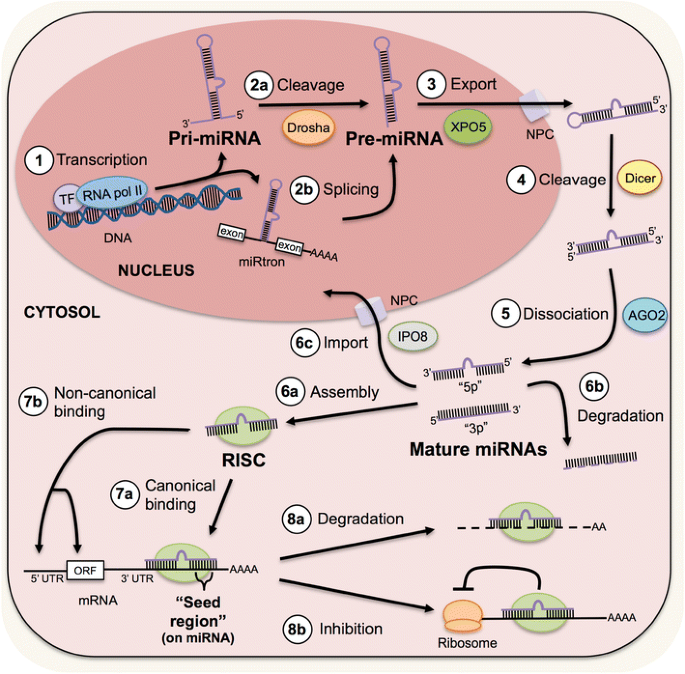
Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow



Different Seed Match Regions Of Mirnas Mirnalyze Follows A Download Scientific Diagram
MiRNAs display perfect pairing in the seed region, between nucleotides 2 and 8, and imperfect hybridization in the central region, between nucleotides 9 and 12 (Lewis et al, 05;Seed region The chemical modifications of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), PS, and DNA−PS were introduced into all of the seven nucleotides of the seed region of the siRNA guide strand (Figure 2b) In addition, 3 (positions 4−6), 5 (positions 3−7), and 7 (seedKeywords RNAi, Offtarget effects, Data analysis, Seed region, miRNA, siRNA, shRNA, Highthroughput screening Background RNA interference (RNAi) is a posttranscriptional gene regulatory mechanism 1 that has been widely used for functional genomics studies both in cell lines and organisms The synthetic duplexes referred to as small inter


The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects


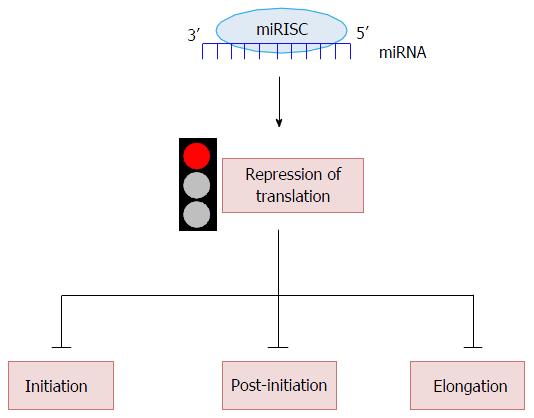
Role Of Micrornas In Translation Regulation And Cancer



The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science



Snps In Microrna Target Sites And Their Potential Role In Human Disease Open Biology


Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics


Predicting Effective Microrna Target Sites In Mammalian Mrnas Elife



Crispr Screening Strategies For Microrna Target Identification Yang The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
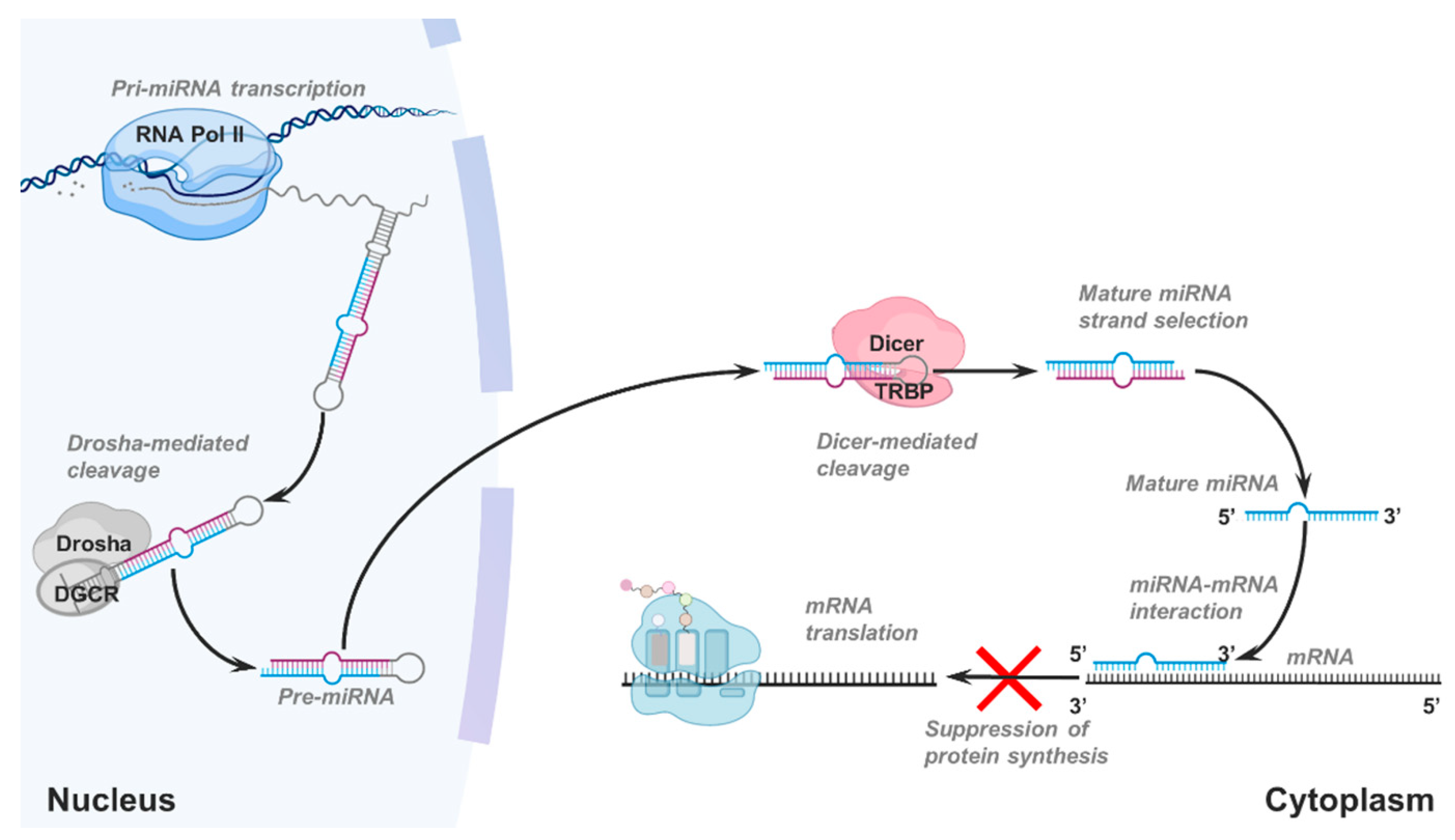


Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html



The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science



Microrna Wikipedia



Introduction To Micrornas Ibiology



Mirpro A Novel Standalone Program For Differential Expression And Variation Analysis Of Mirnas Abstract Europe Pmc



Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow



Riboxx Rna Technologies Better Silencing With Rnai Cap



Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Li Human Mutation Wiley Online Library



Examples Of Mirna Target Interactions Pairing Schemes Open I
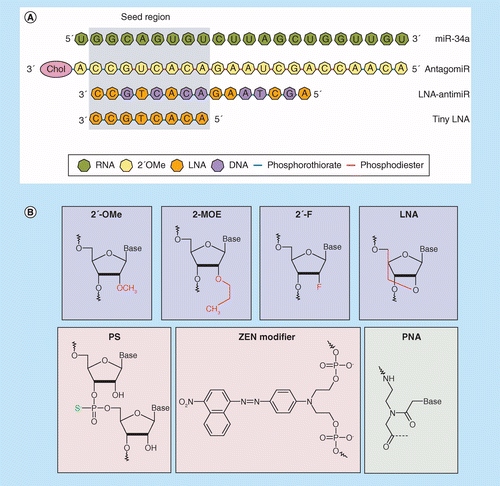


Mirna Therapeutics A New Class Of Drugs With Potential Therapeutic Applications In The Heart Future Medicinal Chemistry



Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Biorxiv



Tools For Sequence Based Mirna Ta Preview Related Info Mendeley



Human Polymorphism At Micrornas And Microrna Target Sites Pnas



Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal
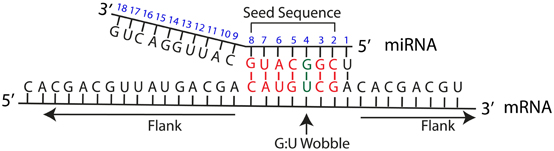


Frontiers Common Features Of Microrna Target Prediction Tools Genetics
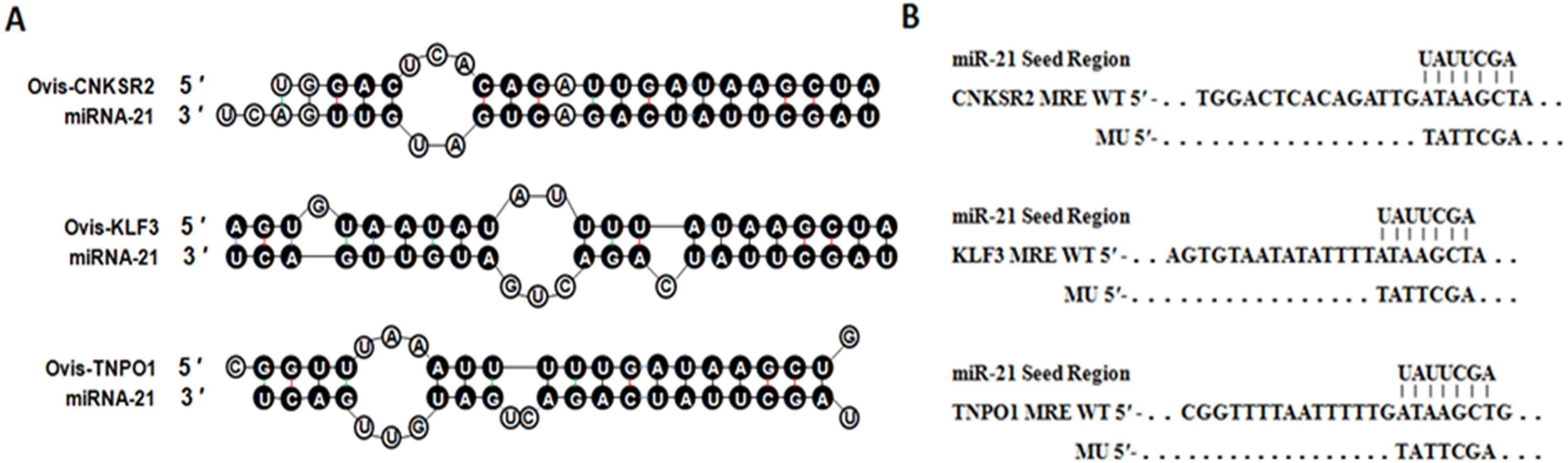


Identification Of Microrna 21 Target Genes Associated With Hair Follicle Development In Sheep Peerj



Muscle Stem Cell Behavior Is Modified By Microrna 27 Regulation Of Pax3 Expression Pnas



3 Uridylation Confers Mirnas With Non Canonical Target Repertoires Sciencedirect



A Microrna Guide For Clinicians And Basic Scientists Background And Experimental Techniques Heart Lung And Circulation



Mirna Microrna Target Prediction Validation And Functional Abm Inc


Micrornas Sound Off Genome Medicine Full Text


Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics


Targetscan Non Canonical Sites



Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal


New Insights Into The Function Of Mammalian Argonaute2



Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect



Helix 7 In Argonaute2 Shapes The Microrna Seed Region For Rapid Target Recognition The Embo Journal



Mirbase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Role Of Micrornas In Translation Regulation And Cancer



Mirna Targeting Growing Beyond The Seed Trends In Genetics


Microrna Mediated Target Mrna Cleavage And 3 Uridylation In Human Cells Scientific Reports



Different Mirna Mrna Seed Site Interaction Patterns 6m Open I



Mirmap



Types Of Mirna Target Sites And Multiple Sites A Stringent Seed Download Scientific Diagram



Chemical Modifications In The Seed Region Of Mirnas 221 222 Increase The Silencing Performances In Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells Sciencedirect



The Characterization Of Microrna Mediated Gene Regulation As Impacted By Both Target Site Location And Seed Match Type


Microrna Wikipedia
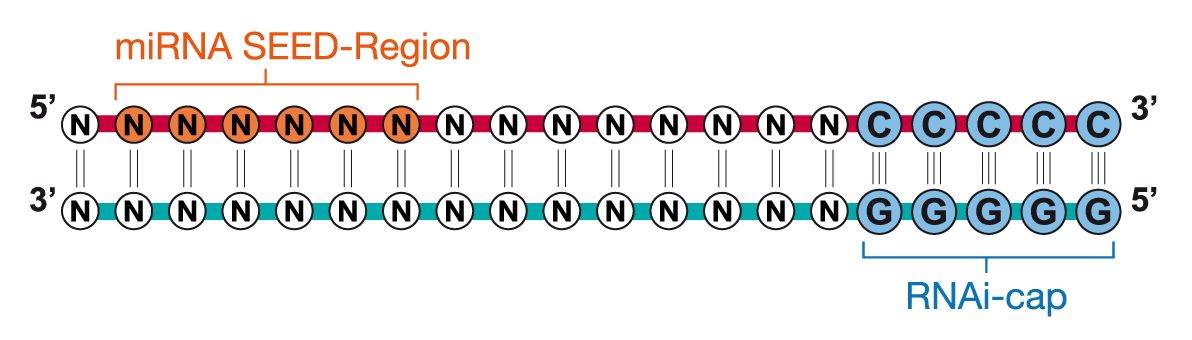


Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna


Principles Of Microrna Target Recognition



Mirna Seed Types Nine Seed Types Are Categorized In Two Groups Download Scientific Diagram
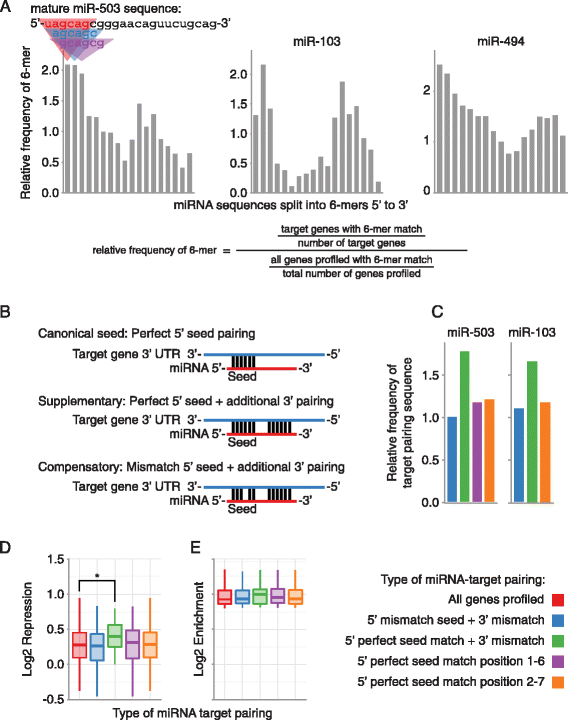


Mir 503 Represses Human Cell Proliferation And Directly Targets The Oncogene Ddhd2 By Non Canonical Target Pairing Bmc Genomics Full Text
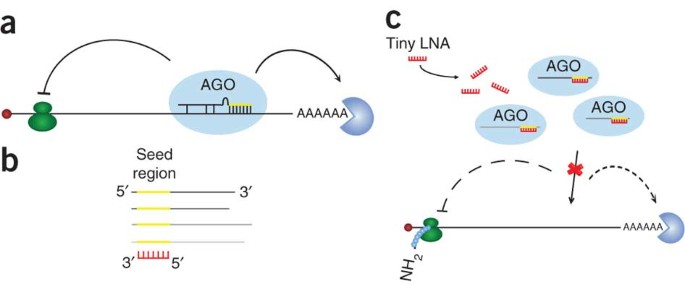


Silencing Of Microrna Families By Seed Targeting Tiny Lnas Nature Genetics
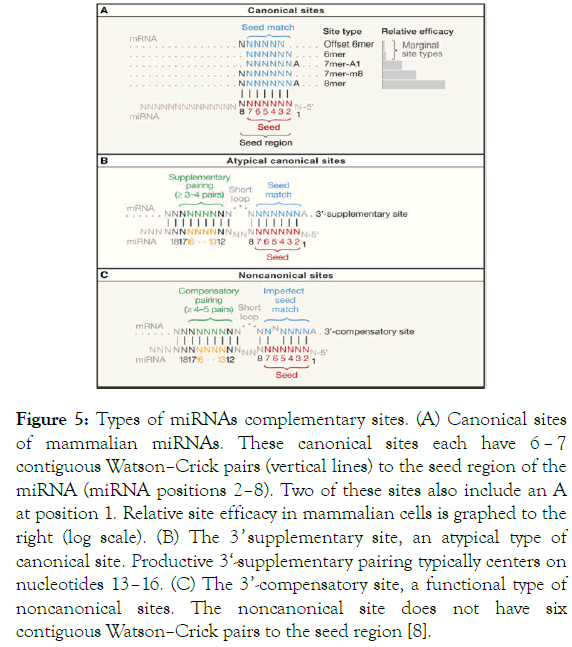


Micrornas In Skin Biology Biogenesis Regulations And Functions In Homeostasis And Diseases



Snps In Microrna Target Sites And Their Potential Role In Human Disease Open Biology



Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal


Micrornas In Injury And Repair Springerlink
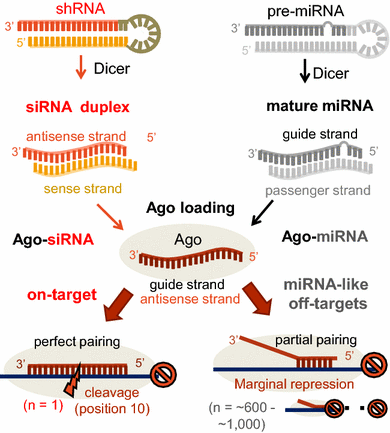


Evaluation And Control Of Mirna Like Off Target Repression For Rna Interference Springerlink



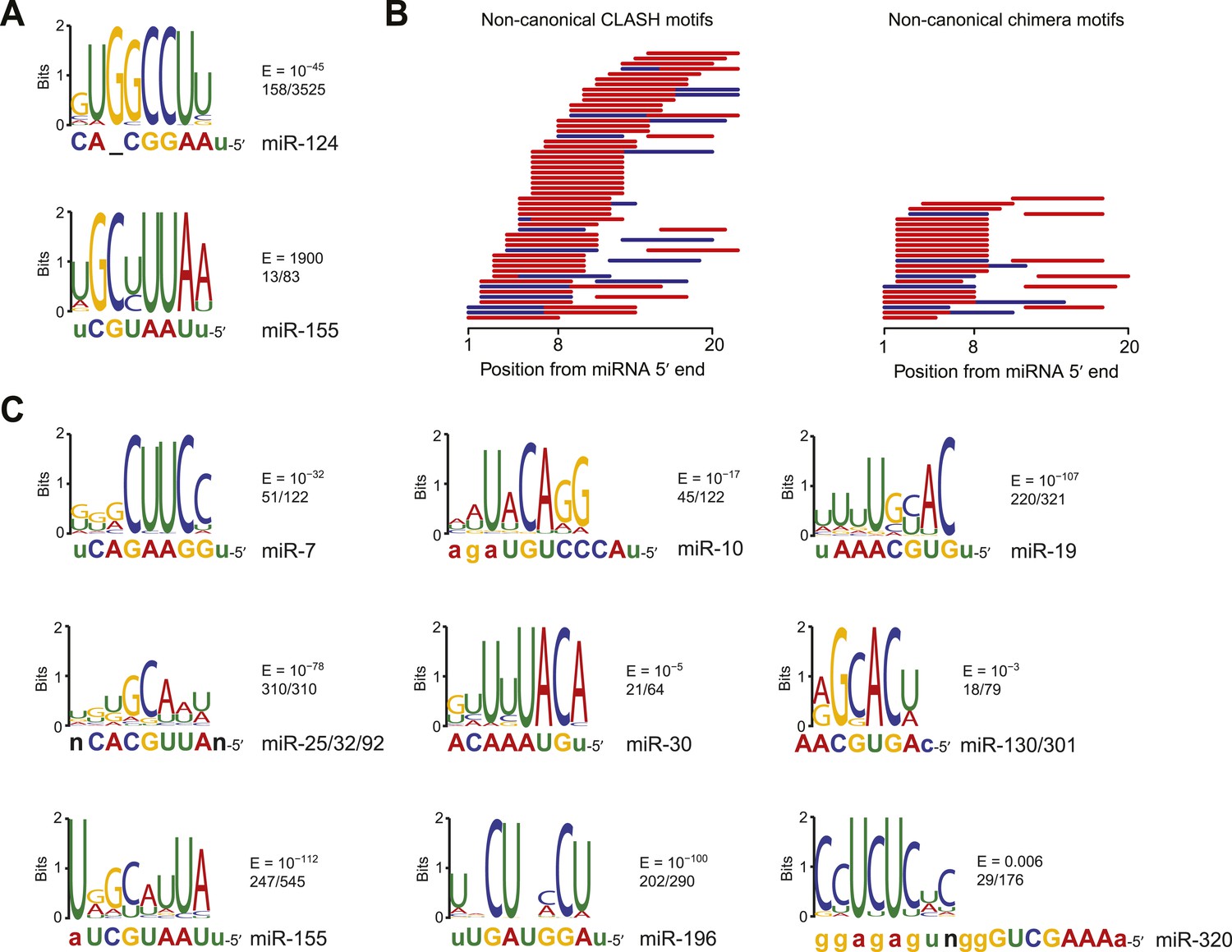
Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell


Miraw A Deep Learning Based Approach To Predict Microrna Targets By Analyzing Whole Microrna Transcripts



Function Control Of Anti Microrna Oligonucleotides Using Interstrand Cross Linked Duplexes Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



Frontiers In Bioscience 17 2508 2540 June 1 12 Micrornas Molecular Features And Role In Cancer Elodie Lages1 2 Helene Ipas1 2 Audrey Guttin1 2 3 Houssam Nesr1 2 Francois Berger1 2 Jean Paul Issartel1 2 3 4 1inserm U6 Team7
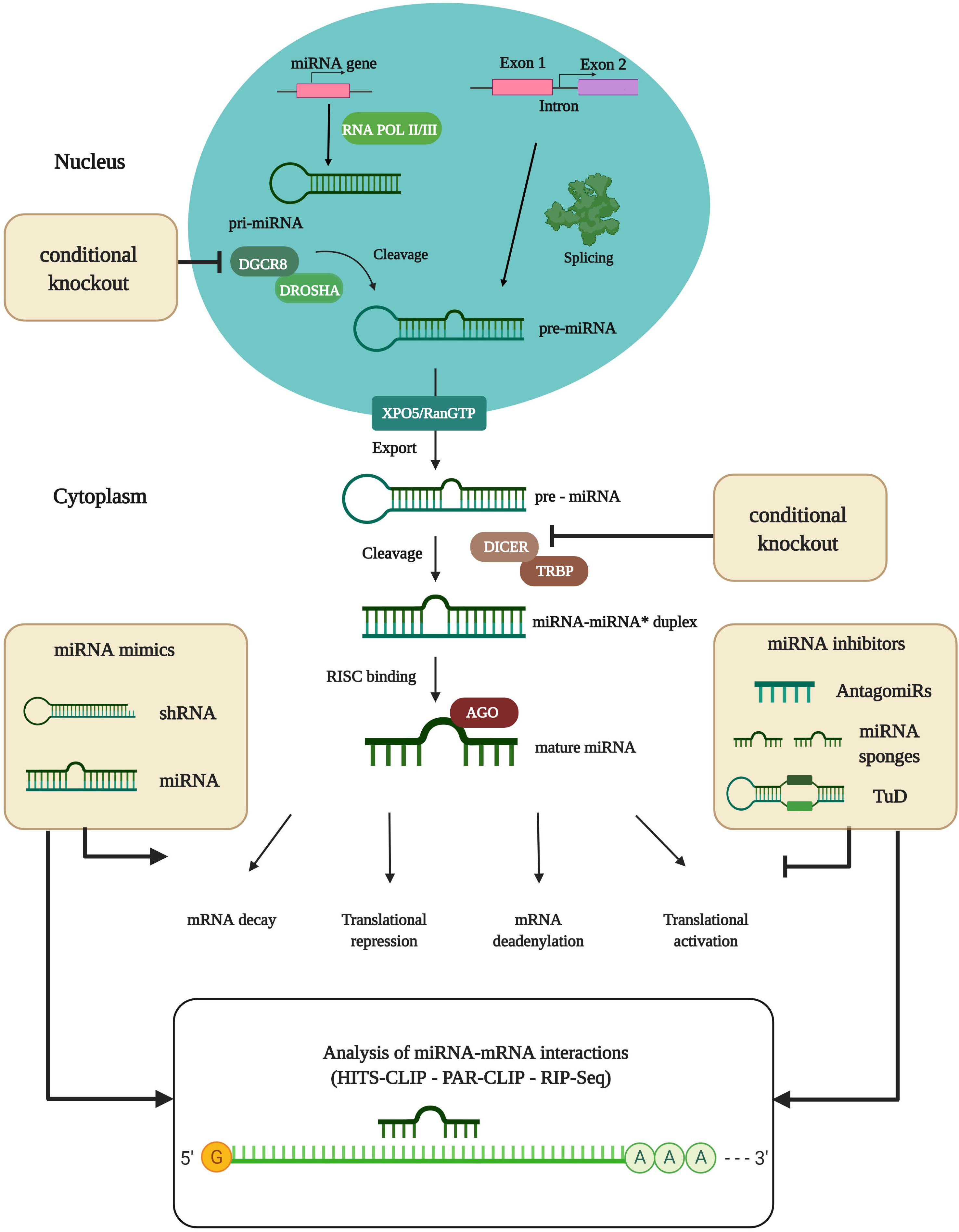


Frontiers Mirna Regulatory Functions In Photoreceptors Cell And Developmental Biology
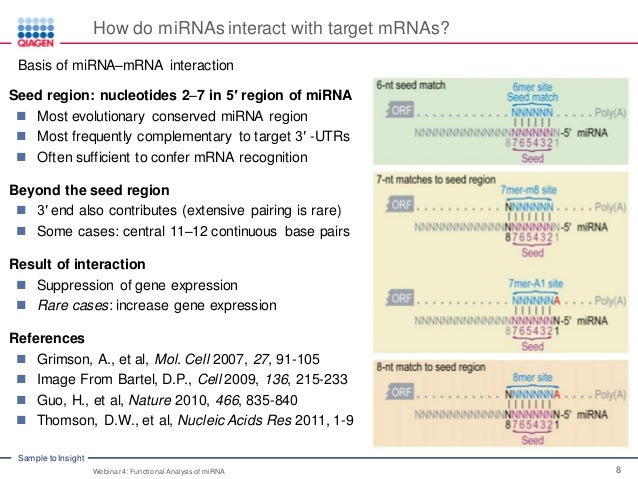


Functional Analysis Of Mirna Mirna And Its Role In Human Disease Web



Complementarity To An Mirna Seed Region Is Sufficient To Induce Moderate Repression Of A Target Transcript In The Unicellular Green Alga Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Yamasaki 13 The Plant Journal Wiley Online Library
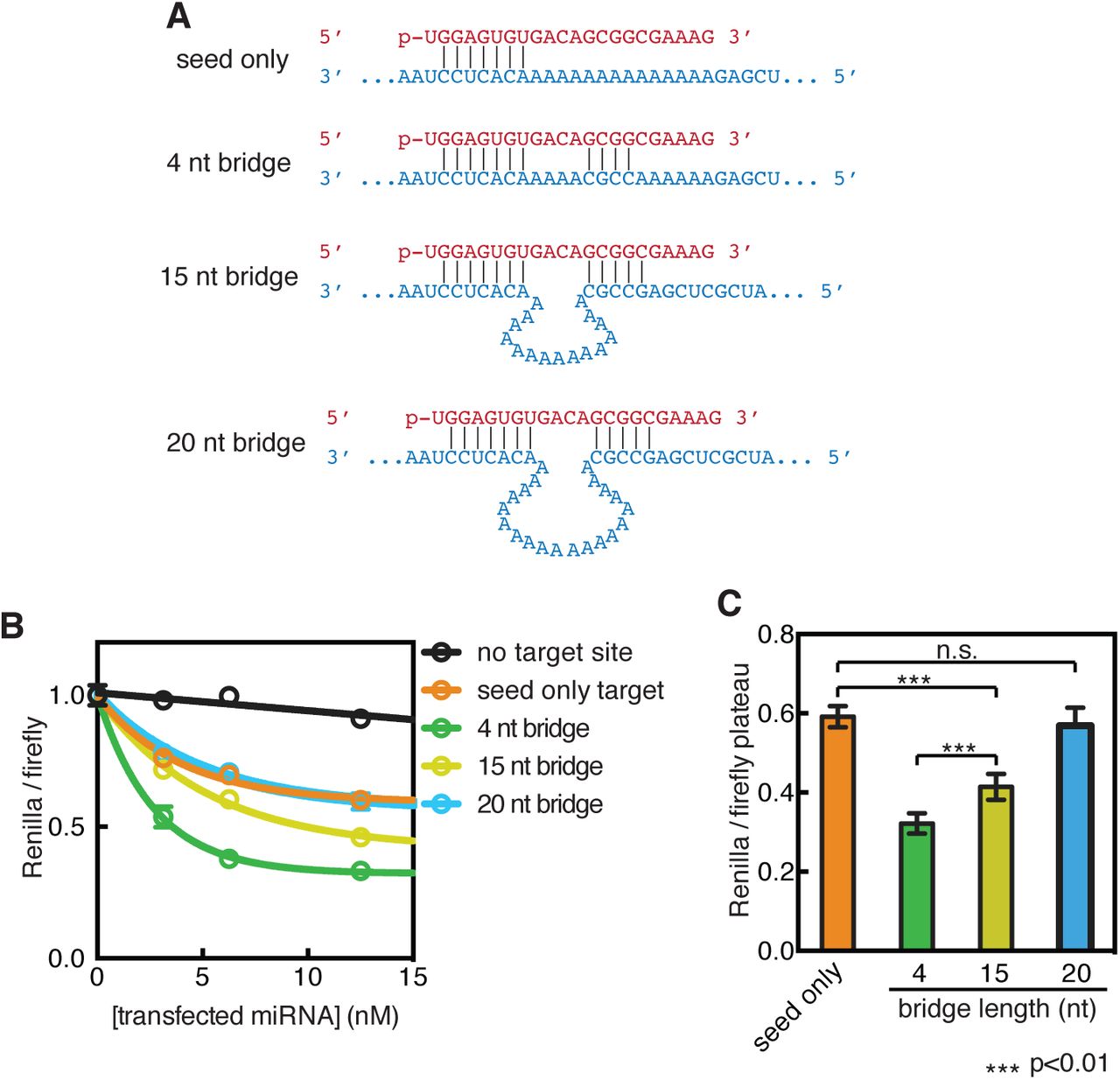


Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting Biorxiv



Miraw A Deep Learning Approach To Predict Mirna Targets By Analyzing Whole Mirna Transcripts Biorxiv


Mir0c Microrna 0c



Clustering Pattern And Functional Effect Of Snps In Human Mirna Seed Regions



Microrna Regulation And Cardiac Calcium Signaling Circulation Research



Rna Interference The Molecules That Govern Genetic Control Young Scientists Journal



Systematic Prediction Of The Impacts Of Mutations In Microrna Seed Sequences
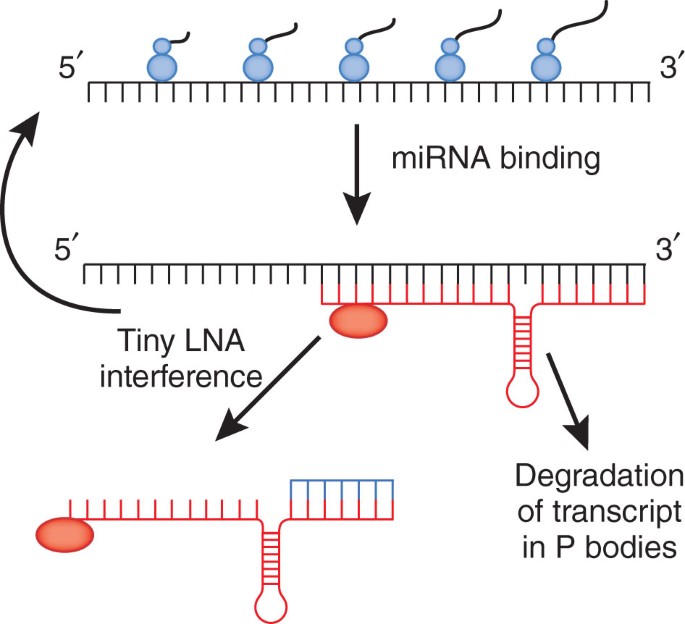


Stopping Rna Interference At The Seed Nature Genetics



Structural Differences Between Pri Mirna Paralogs Promote Alternative Drosha Cleavage And Expand Target Repertoires Sciencedirect
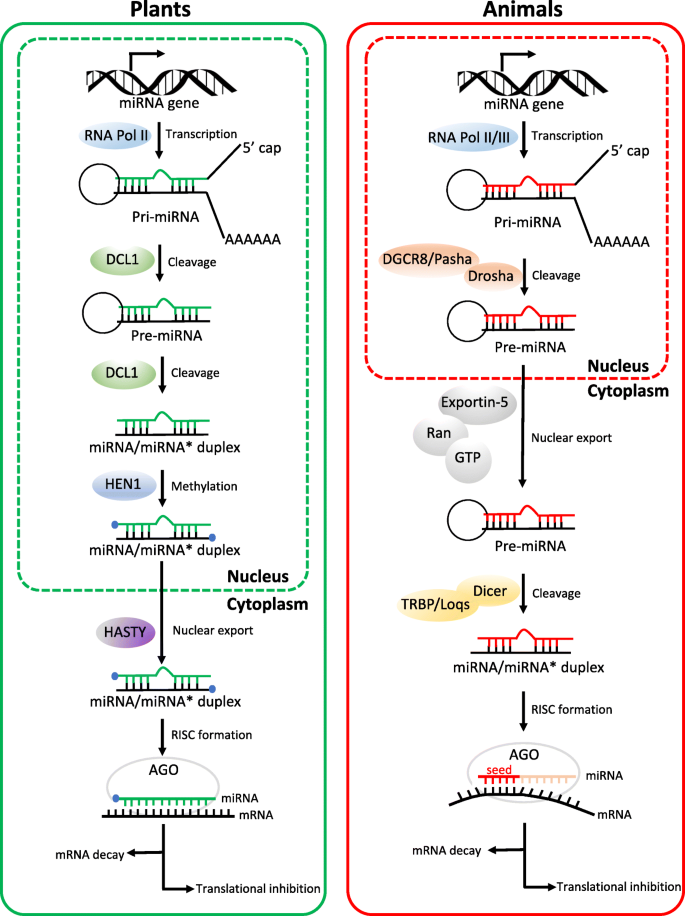


Micrornas From Plants To Animals Do They Define A New Messenger For Communication Nutrition Metabolism Full Text



Sites Matching In The Mirna Seed Region Including All K Mer 8mer Download Scientific Diagram
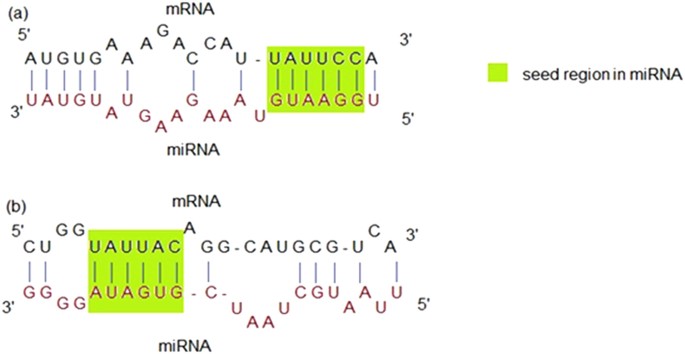


Mirepress Modelling Gene Expression Regulation By Microrna With Non Conventional Binding Sites Scientific Reports



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿